Diagnostic performance of Kaiser score in the evaluation of breast cancer using MRI: A systematic review and meta analysis
Purpose
To assess the performance of Kaiser score (KS) in detecting and characterizing breast cancer on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Methods
The protocol was pre-registered at (https://osf.io/83c6j/). We performed a comprehensive search in PubMed, Embase, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science until 30 October 2024 for studies that used KS for detection of breast cancer on MRI. The risk of bias in the included studies was evaluated utilizing Quality Assessment of Diagnostic Accuracy Studies 2 (QUADAS-2). Diagnostic values of area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, positive and negative likelihood ratios, and diagnostic odds ratio were calculated using a random-effects bivariate model. Meta-regression was used to explore the source of heterogeneity when I2 was ≥ 50 %. P-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Results
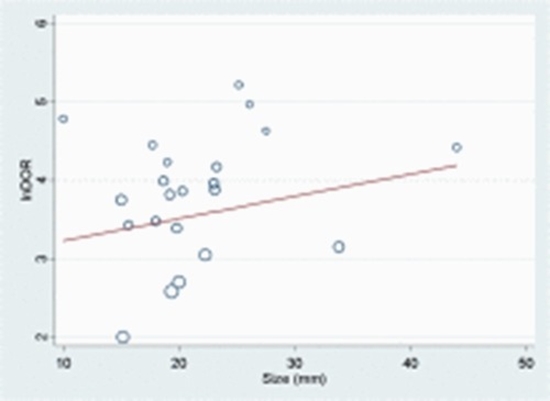
A total of 29 studies with 7918 patients and 8451 breast lesions were included. The pooled sensitivity, specificity, and AUC of KS for detecting malignant breast lesions on MRI were 95 % (95 % CI = 94 % to 96 %), 70 % (95 % CI = 64 % to 75 %), and 0.94 (95 % CI = 0.91 to 0.96), while for Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS), they were 97 % (95 % CI = 92 % to 99 %), 46 % (95 % CI = 30 % to 62 %), and 0.89 (95 % CI = 0.86 to 0.91). Sensitivity difference was not statistically significant (p-value = 0.803), but specificity difference was significant (p-value = 0.001). Also, KS demonstrated slightly better diagnostic accuracy for mass lesions with a sensitivity of 96 % (95 % CI = 94 % to 97 %), specificity of 69 % (95 % CI = 60 % to 77 %), and AUC of 0.96 (95 % CI = 0.94 to 0.97) compared to non-mass lesions with 93 % (95 % CI = 88 % to 96 %), 68 % (95 % CI = 58 % to 77 %), and 0.91 (95 % CI = 0.88 to 0.94) values, respectively. KS showed better performance in larger lesions.
Conclusion
The KS’s superior diagnostic performance compared to BI-RADS, particularly its ability to avoid unnecessary biopsies, makes it valuable for diagnostic and clinical decision-making.






comment